was added to your cart.
Colecalciferol: 5 facts about the Vital Vitamin

Colecalciferol: 5 facts about the Vital Vitamin
Colecalciferol, also known as vitamin D3, plays a pivotal role in maintaining our health and well-being. From bone strength to immune function, this vital nutrient influences various aspects of our physiological functions. Let's explore five key facts about colecalciferol that highlight its importance in our daily lives. We will also dive into the origin of colecalciferol and guide you to finding the right dosis for you.
1. Sunlight Synthesis: Colecalciferol's Natural Source
Colecalciferol is often referred to as the "sunshine vitamin" for a reason. The primary natural source of vitamin D3 is sunlight. When our skin is exposed to ultraviolet B (UVB) rays, a fascinating process unfolds: The sun triggers the synthesis of vitamin D in our skin, converting a compound into its active form, colecalciferol. The time needed to produce sufficient colecalciferol (vitamin D3) through sunlight exposure varies based on factors like geographical location, skin type, and season. In general, spending approximately 10 to 30 minutes in the sun, two to three times a week, with exposed face, arms, and legs, can help many individuals maintain adequate vitamin D levels. However, during some times of the year this is not feasible - that's why colecalciferol supplementation is recommended in most European countries between October and March. (1)
2. Chief Organizer of Calcium Absorption
One of the primary functions of colecalciferol is its crucial role in calcium absorption. Calcium is a fundamental mineral for bone health, and vitamin D3 facilitates its absorption in the small intestine. Without sufficient levels of colecalciferol, the body struggles to absorb calcium efficiently, leading to weakened bones and an increased risk of conditions like osteoporosis. Think of colecalciferol as the chief organizer behind the scenes, making sure calcium gets absorbed properly in the gut. It's like a teamwork routine where vitamin D3 directs the show, ensuring our bones stay strong. Without enough of it, the whole performance gets shaky, and conditions like osteoporosis are more likely to develop. (2)
3. Colecalciferol's role in Immune Support
Colecalciferol acts as a crucial modulator of immune functions. The fat-soluble vitamin is recognized for its ability to enhance the innate and adaptive arms of the immune response. Adequate levels of vitamin D3 contribute to the activation and regulation of immune cells, including macrophages and T lymphocytes, which play key roles in recognizing and combating pathogens. Furthermore, vitamin D3 has been associated with the production of antimicrobial peptides, substances that help the body fend off infections. This multifaceted involvement in immune modulation underscores the importance of maintaining sufficient levels of colecalciferol for a robust and effective immune defense against a range of potential threats. (3)

4. Sources Beyond Sunlight
While sunlight is the primary source, colecalciferol can also be obtained through certain foods. Fatty fish, such as salmon and mackerel contain vitamin D3. Also, fortified dairy products, egg yolks, and some mushrooms contain varying amounts of this essential nutrient. However, the colecalciferol (vitamin D3) intake via natural foods is very limited - internal production of vitamin D3 in the skin is needed to maintain sufficient blood levels.
During the autumn and winter periods taking colecalciferol 4000 IU every 4 days is a common approach to supplementing vitamin D3. Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that can be stored in the body, and the 4000 IU dosage every 4 days is strategically designed to help individuals meet their daily recommended requirement. This approach is based on the concept of cumulative dosing, where the body accumulates vitamin D over the course of several days. By providing a higher dosage less frequently, individuals can ensure a steady supply of vitamin D without the need for daily supplementation. In this scenario, the average daily intake over the 4-day period would be equivalent to the recommended daily requirement. Individuals with extremely low vitamin D levels may be prescribed a higher initial dosage, such as 20000 IU, to rapidly correct the deficiency. Once optimal levels are achieved, the dosage is often adjusted to a maintenance level. (4)
5. Deficiency Risks: Recognizing the Signs
Despite the body's ability to produce vitamin D through sunlight exposure, deficiency remains a prevalent concern. Factors such as limited sunlight exposure, dark skin pigmentation, and certain medical conditions can contribute to lower vitamin D levels. Recognizing the signs of deficiency, which may include muscle weakness, fatigue, and increased susceptibility to infections, is crucial for timely intervention and maintaining overall health.
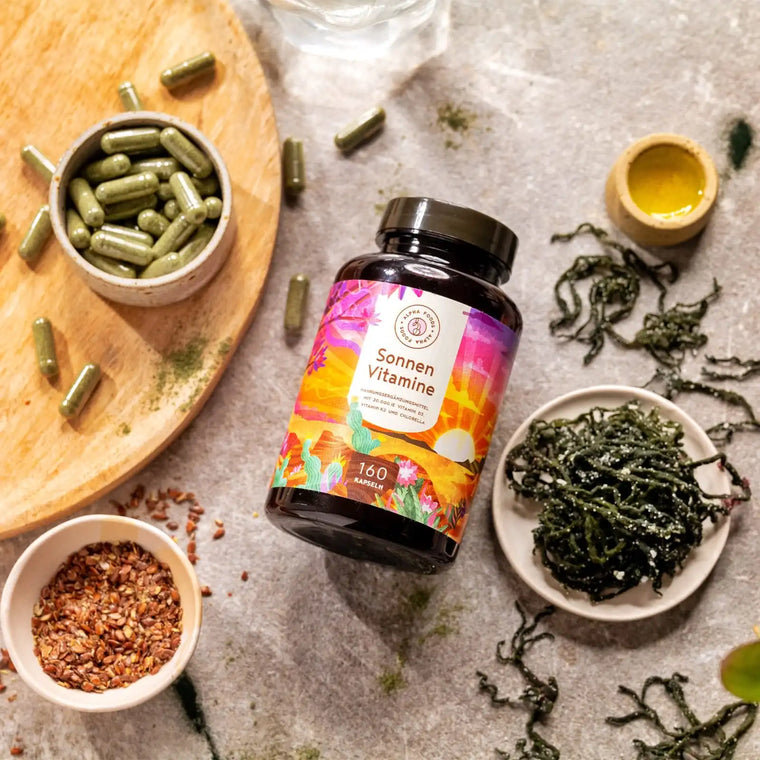
Sun Vitamins from Alpha Foods combines high quality colecalciferol / vitamins D3 with K2 due to their complementary roles in calcium metabolism and bone health. While vitamin D3 enhances the absorption of calcium in the intestines, ensuring an adequate supply for various physiological processes, increased absorption could lead to an accumulation of calcium in soft tissues if not properly regulated. Vitamin K2, specifically its subtypes MK-4 and MK-7, plays a crucial role in directing calcium to the bones and teeth, preventing its deposition in arteries and soft tissues. It activates proteins that help move calcium into the bones, supporting bone mineralization. (5) Apart from the D3 & K2 formula, Sun Vitamins contain omega-3 from linseed oil to optimise the bioavailability of the fat-soluble vitamin D3.

Stefanie Schulz